

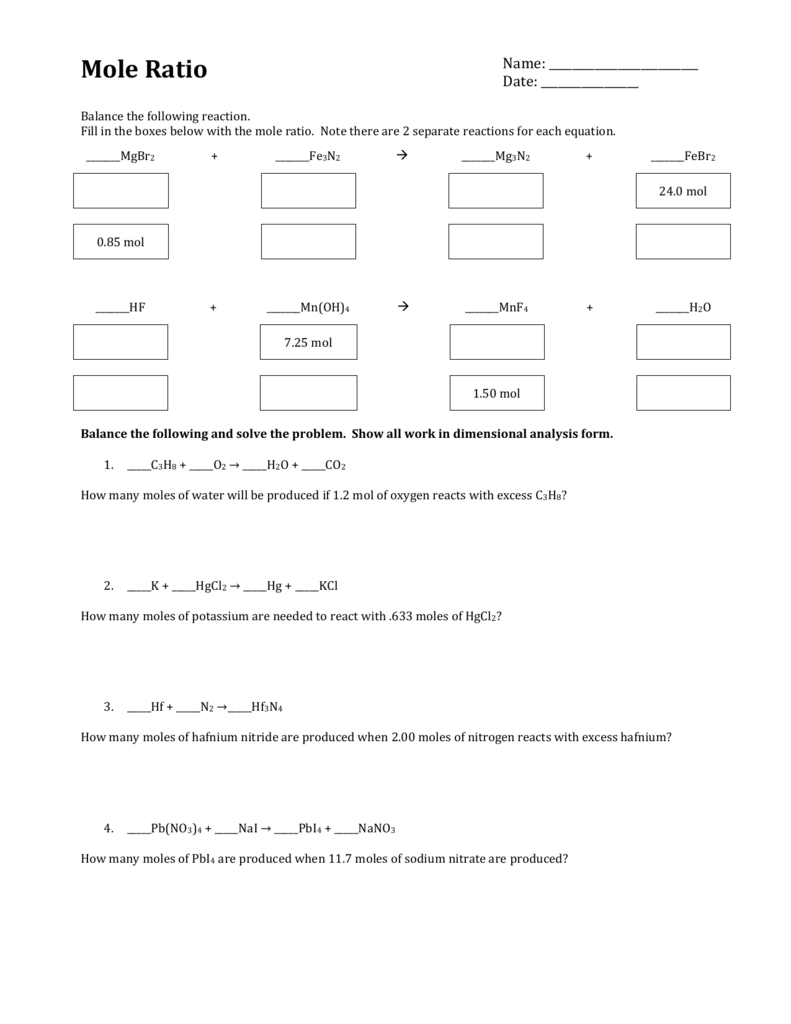
The solid copper metal will settle to the bottom of the beaker. Allow the reaction mixture to stand, without stirring, for 5 minutes to ensure complete reaction. The molarity is calculated using the formula: mass solute/ moles solute molarity. Data Table mass NaHCO moles NaHCO liters NaHCO 7. Calculate the moles of NAHCO in the sample and record the data in the data table. While stirring, slowly add the iron filings to the hot copper(II) sulfate solution. The molarity is calculated using the formula: mass solute/ moles solute molarity 1. Measure and record the exact mass of the filings. Measure approximately 2 g of iron metal filings onto a piece of weighing paper. Using tongs, remove the beaker from the hot plate. Stir until all of the solid is dissolved, but do not boil. Add 50 mL of distilled water to the copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate and heat the mixture on the hot plate at a medium setting. Place approximately 12 g of copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate into the 150-mL beaker and measure and record the combined mass. They are based on the balanced chemical equation. Measure and record the mass of a clean, dry 150-mL beaker. Mole to mole ratios relate the number of moles of any substance in a balanced chemical reaction. Is it important that you know you are using the hydrated form of copper(II) sulfate Would it be possible to use the anhydrous form Why or why not Procedure 1. Be sure to include safety precautions and procedure notes. Prepare all written materials that you will take into the laboratory. Turn off the hot plate when not in use.
CHEMLAB 12 A MOLE RATIO ANSWERS CRACKED
By measuring the mass of iron that reacts and the mass of copper metal produced, you can calculate the ratio of moles of reactant to moles of product. Name Date Class CHEMLAB 12 A Mole Ratio Iron reacts with copper(II) sulfate in a single replacement reaction.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
